
If you experience neck and back conditions, a health professional may recommend a different test to know what is not visible to the naked eye. But how will your health professional knows which exams or tests to refer? Through talking with you about specific health and medical history, neck or back pain signs and symptoms, and doing thorough neurological and physical examinations.
Step 1. The Health and Medical History
The first thing to do is to know the complete information about your health and medical history. The patient must provide detailed and honest information to help your doctor understand the symptoms you are experiencing, including some spine issues.
Step 2. The Physical Examination
During the physical examination, your health care provider will thoroughly examine your spine, particularly paying attention to the most painful parts and those that are already weakened. Whether it's your low back or neck, the range of motion will be examined too while you move your spine or other parts of the body. For example, when you bend backward, forward, or side-to-side, the range of motion in the lower back portion will be keenly observed.
Step 3. The Neurological Examination
The purpose of this examination is to examine the symptoms and pain as they can be related to your nervous system. For example, other reflex response tests may result in an extreme weakness connected with your symptoms.
There are different kinds of diagnostic tests, and the most common areas are explained below.
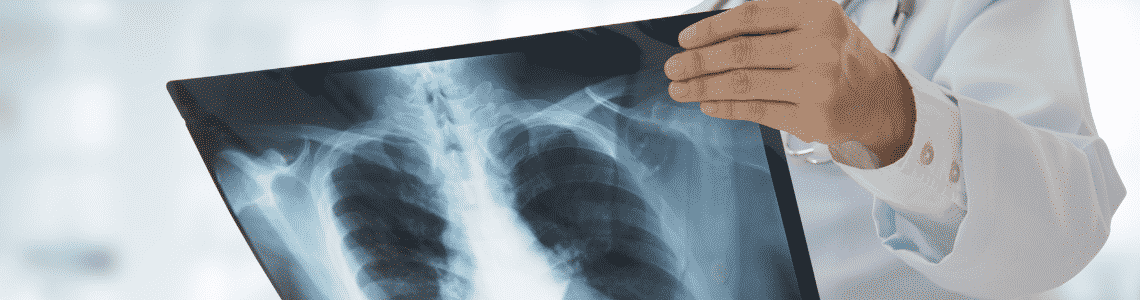
- X-Ray. This process will give you a snapshot of your spine from vital and different directions, back, front, and side. But, X-rays are not a hundred percent effective in conveying soft tissues like the nerves and discs.
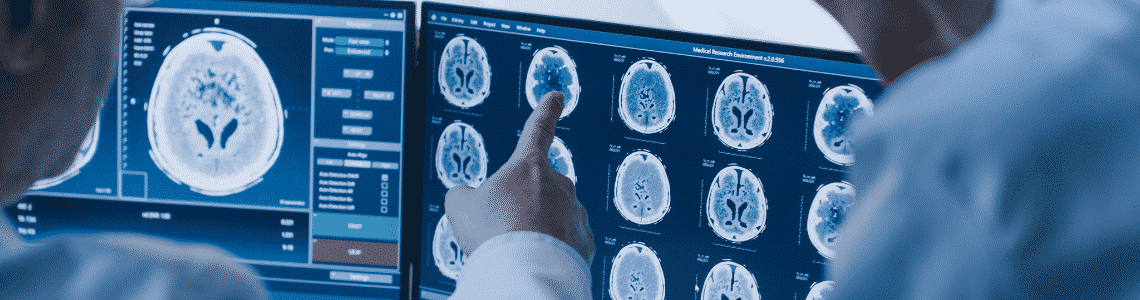
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging or MRI. It uses computer technologies and magnets to produce detailed areas or images of your spinal anatomy. This process can show the structure of every soft tissue in your body, including the spinal cord, nerves, and discs.
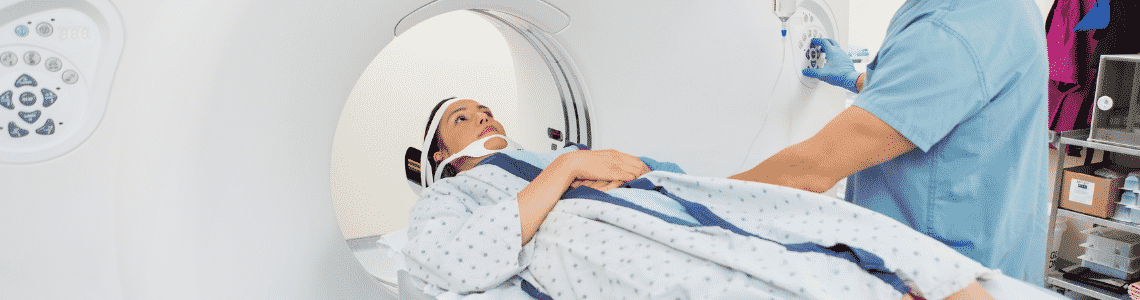
- Computed Tomography or CT Scan. It gives a slice-like image of your spine. The test may differ from the MRI because CT Scan uses radiation to provide more detailed imaging.
Myelogram
- Myelogram or Myelography. The test is mainly done if spinal cord compression is detected. The process starts with a special contrast dye being injected into your spine's dural sac. It is a membrane covering and protecting the spinal cord. After injecting it to the patient, it combines with the spinal produce-fluid, circulating throughout the spine. After that, several MRIs and CT scans are taken to provide the doctor with more explicit images of your spinal cord and other nerve structures.

- Bone Scan. The healthcare provider may ask you for this test for other reasons. The primary purpose is to know more if there is a tumor or spinal fracture. The first step is the IV injection of what they called the 'tracer' or radioactive chemicals. After that, a special camera from the machine used will take pictures of the patient's skeleton to point out changes in the bone.
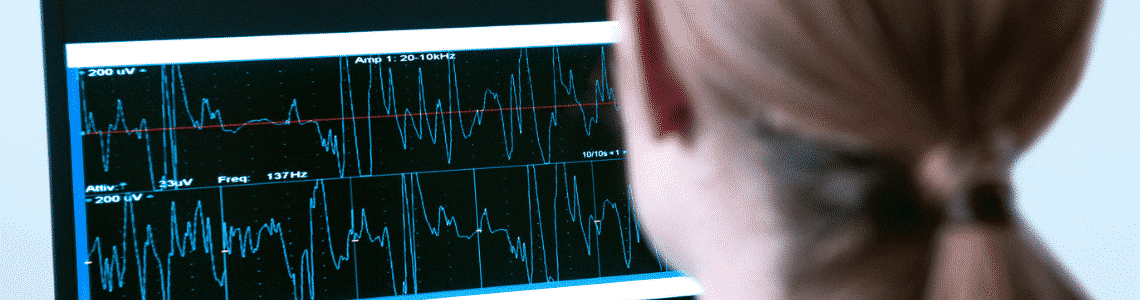
- Electrodiagnostic Studies. An NCV or Nerve Conduction Velocity and EMG or Electromyography tests are commonly done together. The NCV is for nerve function, while EMG is a study test for muscle function.
- Discography. It is a specific test to show if an abnormal or damaged disc is causing the pain. It is not a usual or straightforward routine test. It may only perform before the spinal disc surgery and to assess which disc levels will be treated.
Facet and Medial Blocks. The inflammation between joints can cause pain, especially in your back area. Medial blocks and facets are done by injecting a steroid medication into the joint structures to know if a specific joint causes the pain.
- Fluoroscopy and Cineradiography. It combines x-ray, or conventional fluoroscopy, with video-creating capabilities. Images gathered from these technologies are recorded on a tap and can be replayed, slow motion or one frame in real-time. -either the test will show more musculoskeletal injury like whiplash than a plain or static x-ray. For instance, your healthcare provider can see the spinal structures, like ligaments, discs, and joints moving together.

- Sacroiliac Joint Injection. The sacroiliac joint is found in the lower area of the spine, just above the body's tailbone, is considered the largest joint found in the spine. If there's an inflammation in this area, it can cause buttock and low back pain.
- Diagnostic Spinal Injections. Ct Scans, MRIs, and X-rays provide efficient imaging of several spinal disorders. But, the examinations don't reproduce or show pain. Diagnostic spinal injections are used to control pain and can diagnostically locate the source of pain. It includes discogram or discography, SNRB or selective nerve root blocks, facet joint injections, sacroiliac joint injections, and medial blocks. Usually, these injections provide 6 - 12 hours of relief from the given symptoms and diagnostic results. Remember that if you experience dramatic pain relief, it will only last for 6 hours. But it's still considered positive and correlative results.
New Technologies
There are several inventive medical devices these days that help patients with spinal cord disorders become more mobile and more independent. Some of these devices may also restore the functions of your spines. These include:
Modern wheelchairs
Computer adaptations
Electronic aids
Electrical stimulation devices
Robotic gait training
Conclusion
Doctors or healthcare professionals may ask for different tests and examinations to ensure that you are getting the best result for your spine problems. There are specific blood tests to do as well. It's a good thing that there are several types of medical processes that can help perform the tests and encourage a more detailed and more precise result, not just for the doctors but also for the patients. These days, it’s easier to find means for anything that causes pain to your body. You only have to consider what suited you best, and through a recommendation from healthcare professionals.

